| |
|
|
| |
PRONOUN
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
The words I, You, He, She, It, We and They are personal pronouns. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
a. She
Definition: Refers to a girl, a woman or a female animal.
For example:
- This is Salmah. She is a girl.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
b. He
Definition: Refers to a boy, a man or male animal.
For example:
- This is Syafiq. He is a boy.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
c. You
Definition: Refers to one person or many people you are speaking to.
For example:
- You are tall.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
d. It
Definition: Refers to an object, a plant, a place or an animal.
For example:
- This is a ball. It is round.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
e. I
Definition: Refers to the person speaking or writing.
For example:
- I am jumping.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
f. We
Definition: Refers to a group including the speaker and at least one other person.
For example:
- We are going on a trip.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
g. They
Definition: Refers to people, animals, or things already mentioned or, more generally, to a group of people not clearly described.
For example:
- They are a group of singers.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Possessive adjectives and possessive pronouns are also known as possessive case. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
The word my, your, our, their, her, his and its are possessive adjectives. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
The words mine, his, hers, yours, ours and theirs are possessive pronouns. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
a. Personal Pronouns
i. I
For example:
- I have a book.
ii. He
For example:
- He has a pen.
iii. She
For example:
- She has a car.
iv. You
For example:
- You have a kite.
v. We
For example:
- We have a laptop.
vi. They
For example:
- They have robots.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
b. Possessive Adjectives
i. My
For example:
- That is my book.
ii. His
For example:
- That is his pen.
iii. Her
For example:
- That is her car.
iv. Your
For example:
- That is your kite.
v. Our
For example:
- That is our laptop.
vi: Their
For example:
- That is their robots.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
c. Possessive Pronouns
i. Mine
For example:
- The book is mine.
ii. His
For example:
- The pen is his.
iii. Hers
For example:
- The car is hers.
iv. Yours
For example:
- The kite is yours.
v. Ours
For example:
- The laptop is ours.
vi. Theirs
For example:
- The robots are theirs.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Apostrophe ( ’s ) shows possession.
For example:
- Joshua’s computer is new.
- Angelina’s shoes are beautiful.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| 1.3 |
DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUN |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Demonstrative pronouns are pronouns that point to specific objects. They take the place of a noun, noun phrase, activity, or situation. They always consist of this, these, that, those, and sometimes include none, neither, and such. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
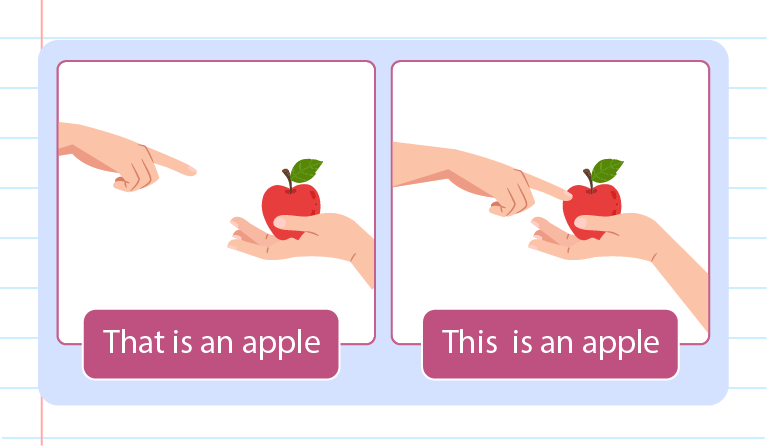
SINGULAR
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
a. This: A person, place, thing that is close by or near. (Singular)
Other example:
This is where he works.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
b. That: A person, place, thing that is at a distance or far. (Singular)
Other example:
That is an aeroplane.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
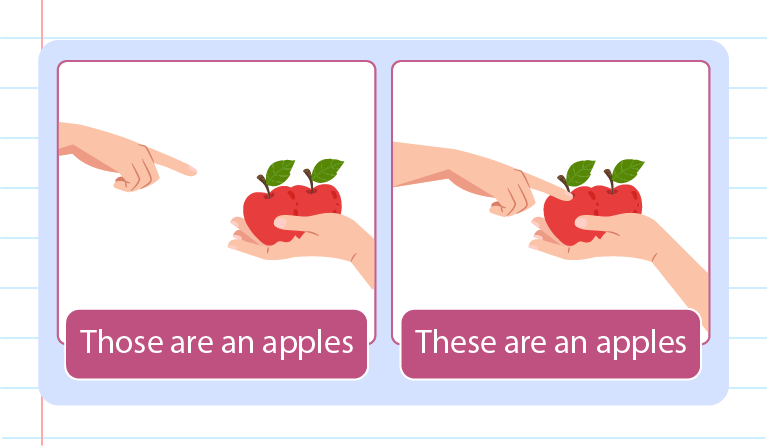
PLURAL
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
a. These: People, places, things that are close by or near. (Plural)
Other example:
These are rolling pins.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
b. Those: People, places, things that are at a distance or far. (Plural)
Other example:
Those are hot air balloons.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| 1.4 |
INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS (WH-QUESTIONS) |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
We use question words to ask certain types of questions. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
a. What
i. Asking for information about something.
- What is your name?
ii. Asking for repetition or confirmation.
- What? I cannot hear you.
- You did what?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
b. Who
Asking what or which person or people (subject).
- Who opened the door?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
c. When
Asking about time.
- When did he leave?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
d. Where
Asking in or at what place or position.
- Where do they live?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
e. Which
Asking about choice.
- Which colour do you want?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
f. Why
Asking for reason, asking what...for.
- Why do you say that?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
g. Whom
Used as the object of a verb or after a preposition when referring to a particular person or when adding information about a person just mentioned.
- He took out a photo of his son, whom he adores.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
h. Whose
Asking about ownership.
- Whose are these keys?
- Whose turn is it?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
i. How
i. Asking about manner.
- How does this work?
ii. Asking about condition or quality.
- How was your exam?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
EXTRA NOTES |
|
| |
|
|
| |
How + adjective / adverb: Asking about extent or degree.
i. How far: Distance.
- How far is Pattaya from Bangkok?
ii. How long: Length (time or space).
- How long will it take?
iii. How many: Quantity (countable).
- How many cars are there?
iv. How much: Quantity (uncountable).
- How much money do you have?
v. How old: Age.
- How old are you?
vi. How come: (Informal) asking for reason, asking why.
- How come I can't see her?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
A reflexive pronoun is used when we refer back to the subject of the sentence. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Reflexive pronouns end in '-self' (singular) or '-selves' (plural).
For example:
- Yoona volunteers herself to help the children with disabilities.
- They were sitting around the fire and trying to keep themselves warm.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Subject Pronoun |
Reflexive Pronoun |
| I |
Myself |
| You |
Yourself / Yourselves |
| They |
Themselves |
| We |
Ourselves |
| He |
Himself |
| She |
Herself |
| It |
Itself |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
We use 'by' before a reflexive pronoun to show that action is done without help.
For example:
a. Janet did all the work by herself.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
We use relative pronoun to join sentences. Most commonly used relative pronouns include who, whom, which, that and whose. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
'Who' is used as the subject of the verb. We use 'who' for people. It is usually followed by a verb.
For example:
a. He is the man.
b. He helped me yesterday.
a + b = He is the man who helped me yesterday.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
'Whom' is used as an object of the verb. We use 'whom' for people. It is usually followed by a noun or a pronoun.
For example:
a. The boy is my cousin.
b. I gave him some books.
a + b = The boy, whom I gave some books to, is my cousin.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
'Which' is used to refer to animals or things. It can be used as the subject or an object of the verb.
For example:
a. That is the hotel.
b. It burnt down last night.
a + b = That is the hotel which burnt down last night.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
'That' is used for people, things and animal.
For example:
- Is this the train that goes to Braintree?
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
'Whose' is used to show the possessions of the people or animals.
For example:
- Do you know whose car that is?
|
|
| |
|
|