| 2.2 |
The Movement and Exchange of Gases in The Human Body |
| Definition |
|
Oxygen and carbon dioxide gas exchange occurs in the alveoli in the lungs and is transported using red blood cells to all cells of the body
|
The process of gas exchange in the alveoli and cells of the body:

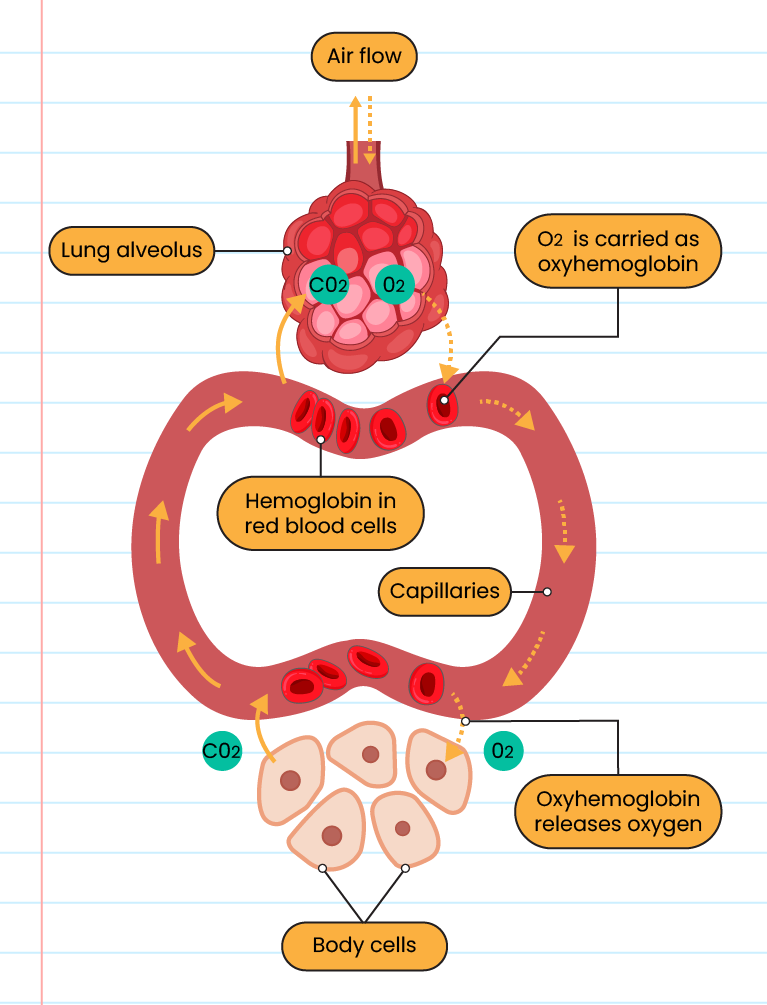
-
The high oxygen content in the alveoli causes the process of oxygen diffusion into the blood capillaries to occur
-
In the blood capillaries, oxygen combines with hemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin
-
The oxyhaemoglobin is transported using red blood cells to all cells of the body and oxygen is released
-
In the cells of the body, the process of oxidation (cellular respiration) takes place to produce energy and carbon dioxide
-
The carbon dioxide permeates from the cells into the capillary tissue and is subsequently transported to the lungs for elimination
The adaptation of alveolar structure to maximize gas exchange:

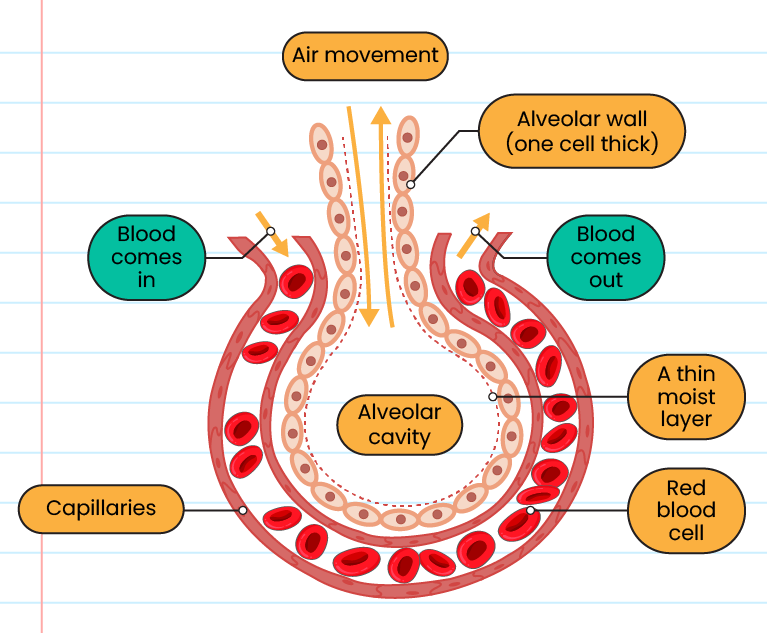
-
A large surface area for gas exchange in the alveoli can increase the oxygen content
-
The surface of the alveoli is moist so that gas easily permeates out and into the alveoli
-
The alveoli are thin-walled as thick as one cell to facilitate gas prescription
-
The alveoli are surrounded by a network of blood capillaries to facilitate rapid gas transport