| 3.2 |
Blood Circulatory System |
| Definition |
|
A tubular system that has pumps and valves that consist of three components, namely the heart, blood vessels, and blood to ensure blood flow occurs in one direction only
|
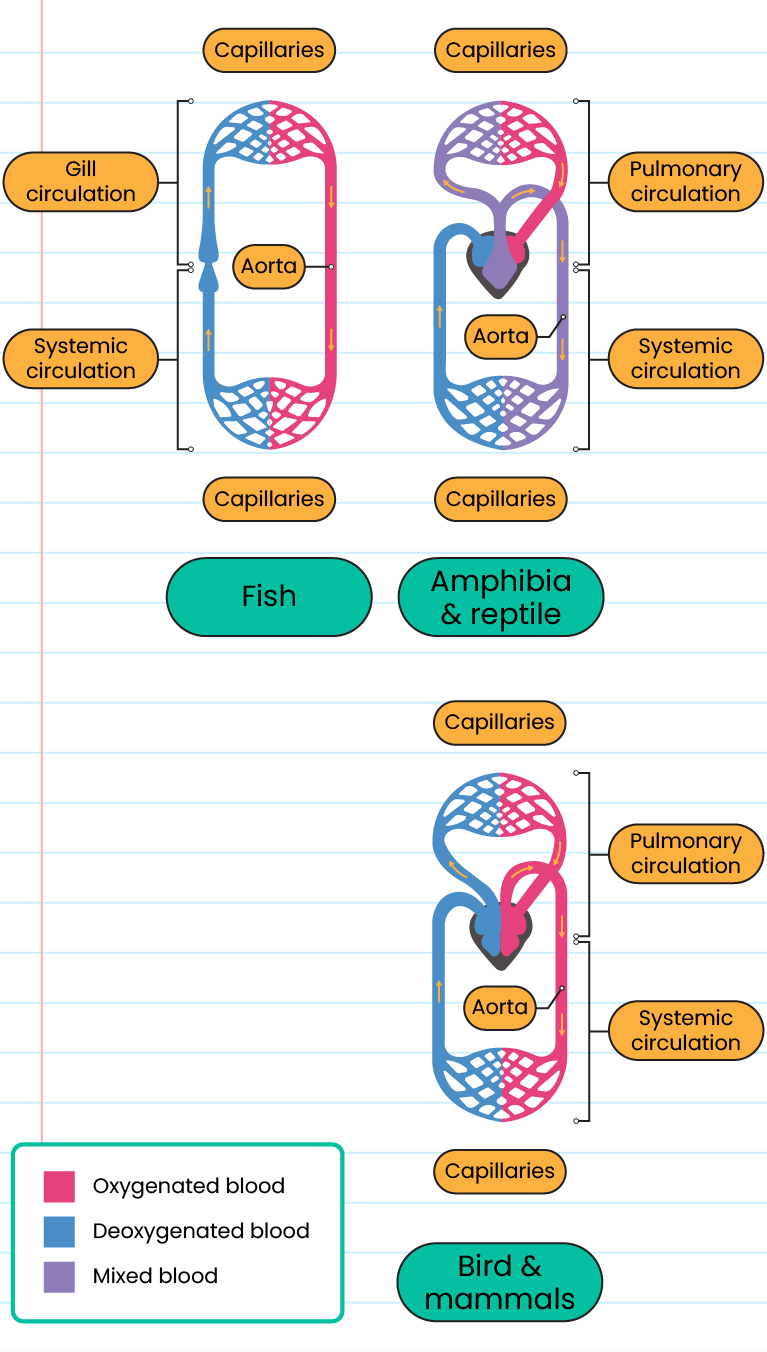
The circulatory system for 3 classes of vertebrates:

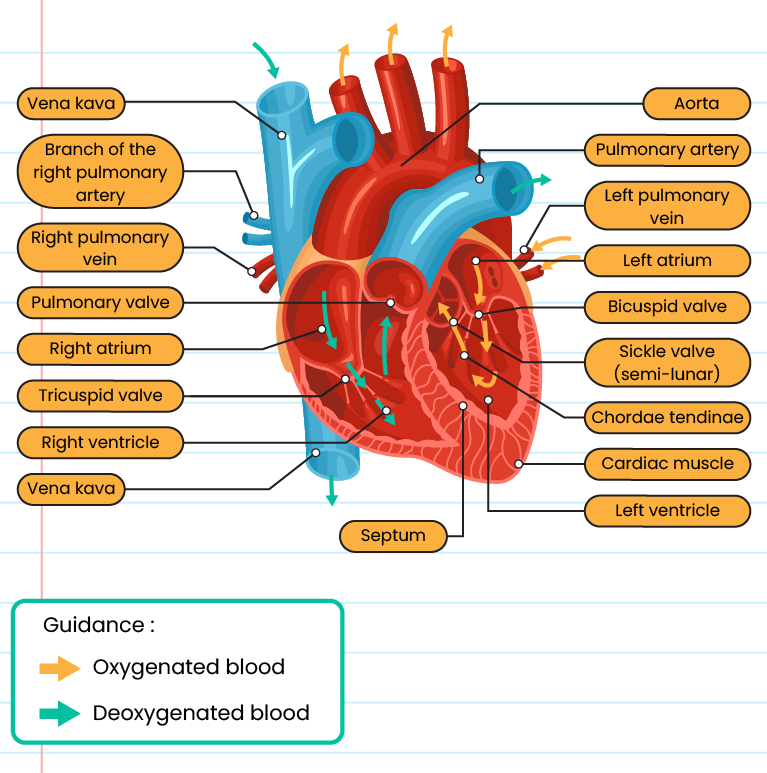
The structure and function of the human heart:

|
Structure
|
Function
|
|
Left atrium
|
Pumping oxygenated blood to the left ventricle
|
|
Right atrium
|
Pumping deoxygenated blood to the right ventricle
|
|
Left ventricle
|
Pumps blood to all parts of the body except the lungs
|
|
Right ventricle
|
Pumping deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
|
|
Vena cava
|
Carries deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body to the right atrium
|
|
Pulmonary artery
|
Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
|
|
Aorta
|
Carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to all parts of the body (largest artery)
|
|
Pulmonary vein
|
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
|
|
Septum
|
Isolate the left chamber and the right chamber of the heart
|
|
Tricuspid valve
|
Prevents the recirculation of blood from the right ventricle to the right atrium during ventricular contraction
|
|
Bicuspid valve
|
Prevents the re-flow of blood into the left ventricle from the left atrium during ventricular contraction
|
|
Sickle valve
|
Prevents the re-flow of blood to the ventricles when the ventricles relax
|
The functional efficiency of the human heart:
-
The heart wall is built of cardiac muscle that can contract and relax rhythmically
-
The ventricle has a thicker wall and contracts more strongly than the atrium
-
Has a valve that keeps the blood flowing in one direction only
-
Has a septum that ensures oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood do not mix
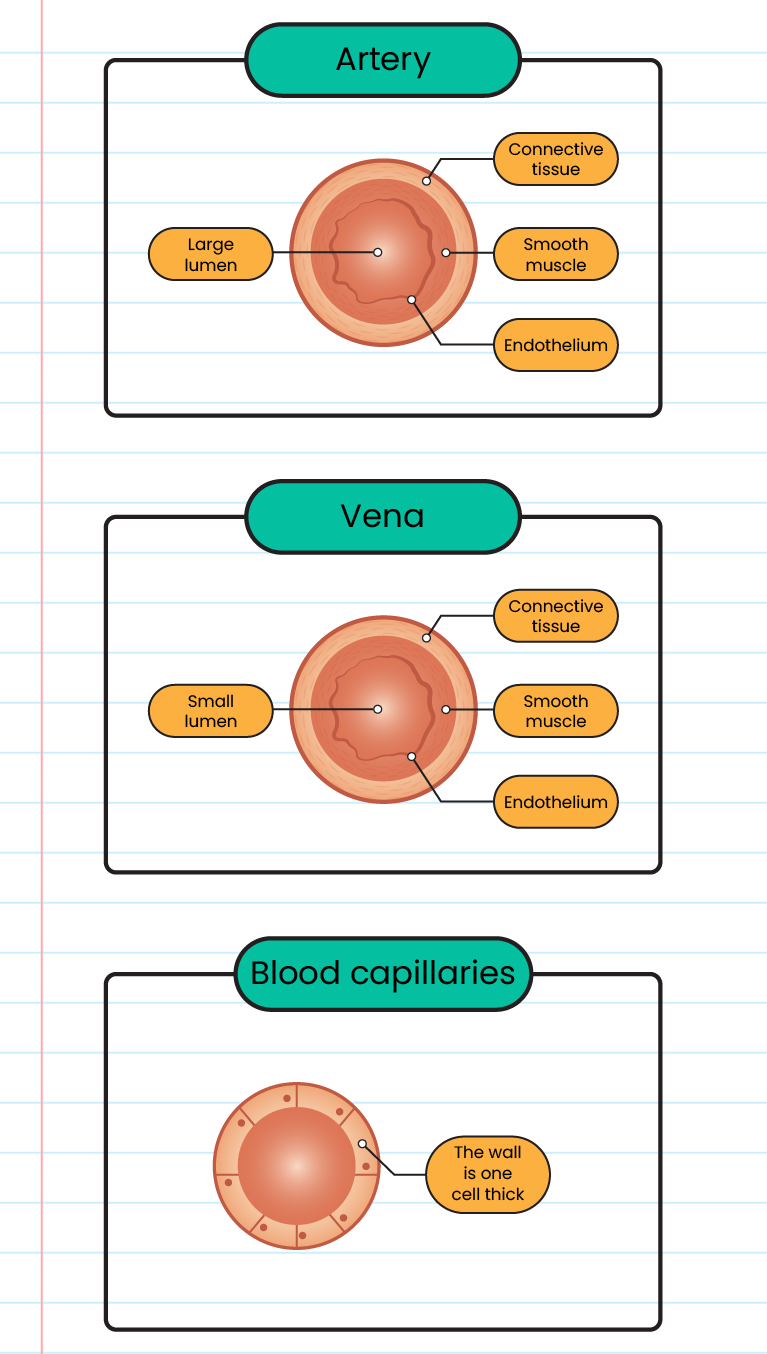
The structure and function of human blood vessels:

|
Types of blood vessels
|
Vena
|
|
Function
|
Brings blood to the heart
|
|
Lumen size
|
Big
|
|
Wall thickness
|
- Thin
- Less muscular
- Less elastic
|
|
Valve
|
There is
|
|
Blood flow
|
Slow and under very low pressure
|
|
Type of blood transported
|
The blood is deoxygenated except the pulmonary veins
|
|
Types of blood vessels
|
Blood capillaries
|
|
Function
|
- Connecting arteries and veins
- Allows the exchange of substances between the blood and body cells
|
|
Lumen size
|
Very small
|
|
Wall thickness
|
The wall is one cell thick
|
|
Valve
|
None
|
|
Blood flow
|
Very slow and under very low pressure
|
|
Type of blood transported
|
Both types of blood is oxygenated and deoxygenated
|
|
Types of blood vessels
|
Artery
|
|
Function
|
Bringing blood out of the heart
|
|
Lumen size
|
Small
|
|
Wall thickness
|
- Thick
- Muscular
- Elastic
|
|
Valve
|
None
|
|
Blood flow
|
Fast and under very high pressure
|
|
Type of blood transported
|
Oxygenated blood except for pulmonary arteries
|
The human circulatory system:
-
The human circulatory system is a closed tubular system that is pumped throughout the body
-
Double circulatory system
-
Pulmonary circulation - blood is transported from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
-
Systemic circulation - blood is transported from the heart to other parts of the body (except the lungs) and back to the heart
The blood pressure:
-
The pressure exerted on the walls of blood vessels due to blood circulation
-
Two readings, namely systolic reading (upper number) and diastolic reading (lower number)
| |
Systolic readings
|
Diastolic readings
|
|
Low blood pressure
|
Under 90
|
Under 60
|
|
Normal
|
90 - 120 mmHg
|
60 - 80 mmHg
|
|
Pre high blood pressure
|
120 - 139 mmHg
|
80 - 89 mmHg
|
|
High blood pressure
|
140 - 160 mmHg
|
90 - 100 mmHg
|
The systole and diastole:
-
When the heart beats, there are two phases namely the diastolic phase and the systolic phase
-
Diastolic phase - the ventricles relax and blood fills the ventricles
-
Systolic phase - the ventricles contract and blood fills the ventricles
-
Lub dub sounds result from closed tricuspid and bicuspid valves (lub) and closed sickle valves (dub)
The factors that affect the heart rate:
|
Gender
|
Females have higher pulse rates than males due to small body size and less muscle mass
|
|
Age
|
The normal pulse rate for adolescents at rest is 75/min and lower for the elderly
|
|
Health rates
|
Healthy individuals have low pulse rates at rest
|
|
Activity fitness
|
During vigorous activity, the pulse rate increases
|
The cardiac care measures:
-
Reduce salt and sugar in food
-
Control blood pressure and diabetes
-
Exercise regularly at least five times a week
-
Eat vegetables and fruits