| 1.2 |
Stimulus and Response in Humans |
| Definition |
|
Sensory organs are organs that can detect stimuli
|
Humans have five sensory organs:
-
Skin (touch)
-
Nose (smell)
-
Tongue (taste)
-
Ears (hearing)
-
Eyes (Sight)
The function of eyes:
The structure of eyes:

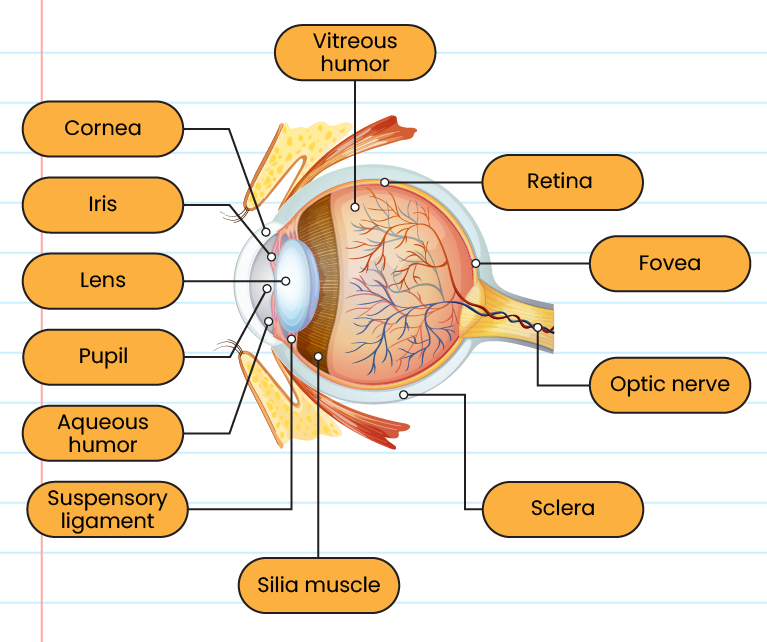
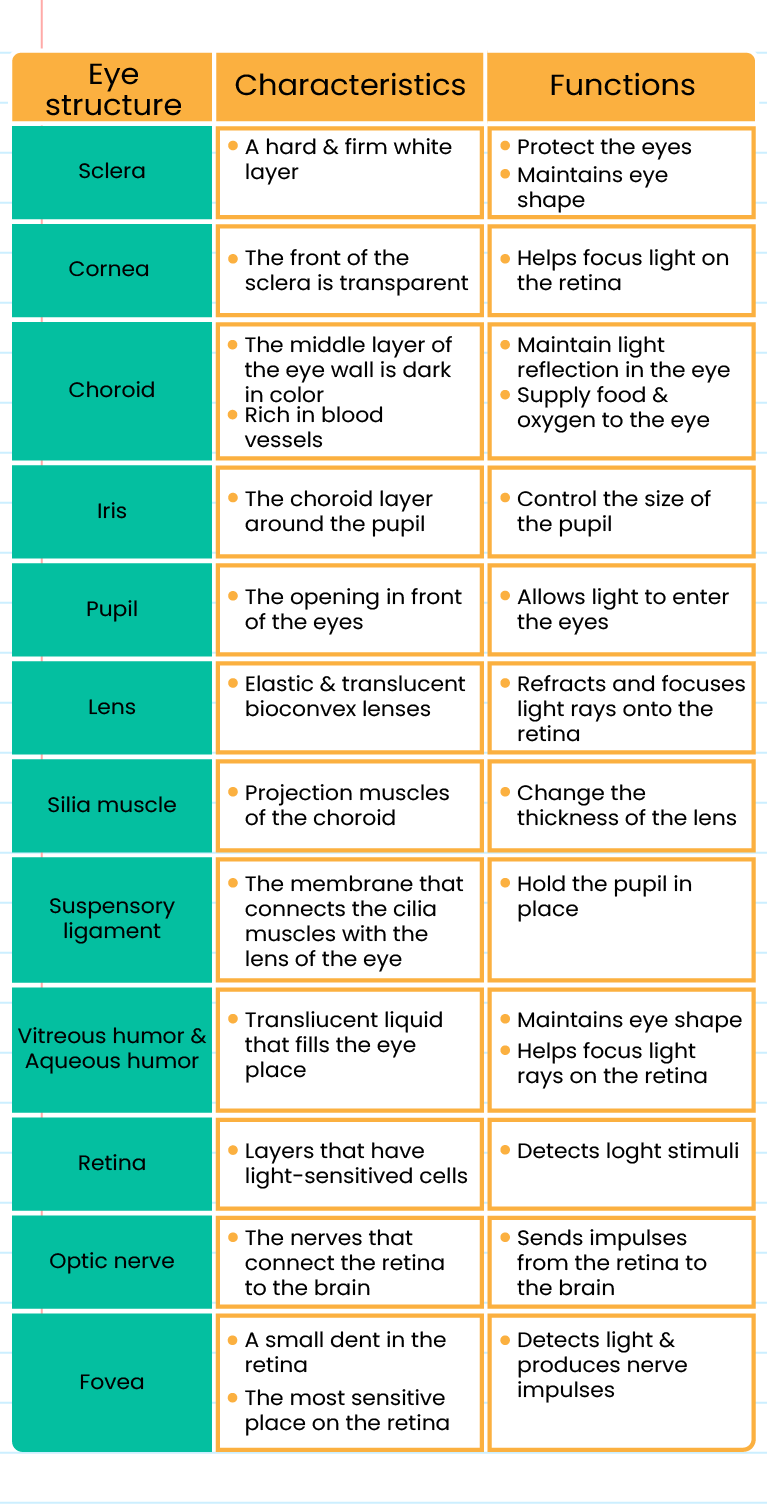
The function of each eyes structure:

The mechanism of vision:
- Light from an object enters the eye through the pupil
-
Light is refracted by the cornea, aqueous humor, eye lens, and vitreous humor
-
Inverted and small images are formed on the retina
-
The retina produces nerve impulses and the optic nerve transmits them to the brain
-
The brain translates impulses and produces upright images
The function of ears:
The structure of ears:

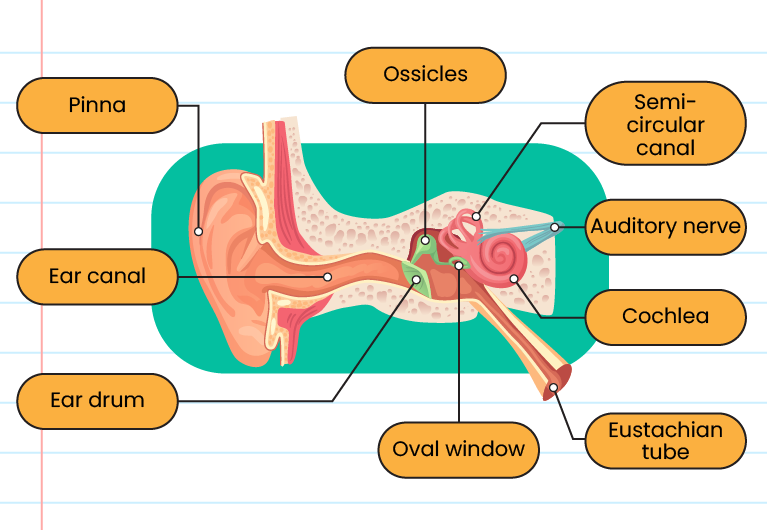
The function of each ears structure:
|
|
The structure of ears
|
Function
|
|
Ossicles
|
Amplifies the vibration of sound and sends it to the oval window
|
|
Earlobe
|
Receives sound waves
|
|
Ear canal
|
Transmits sound waves to the eardrum
|
|
The eardrum
|
Vibrates when sound waves hit it
|
|
Semicircular canal
|
Controls body balance
|
|
The auditory nerve
|
Sends impulses from the cochlea to the brain
|
|
Cochlea
|
Converts sound vibrations into impulses
|
|
Oval window
|
Transmits sound vibrations from the middle ear to the inner ear
|
|
Eustachian tube
|
Balances the air pressure on both sides of the eardrum
|
|
The mechanism of hearing:
-
Sound waves enter the ear canal
-
The eardrum receives sound waves and vibrates
-
The vibrations are amplified by the ossicle bone and transmitted to the oval window
-
The oval windows vibrated
-
The cochlea converts vibrations into impulses
-
Impulses are carried by the auditory nerve to the brain
-
The brain interprets it as sound
The function of the nose:
The structure and mechanism of the nose:

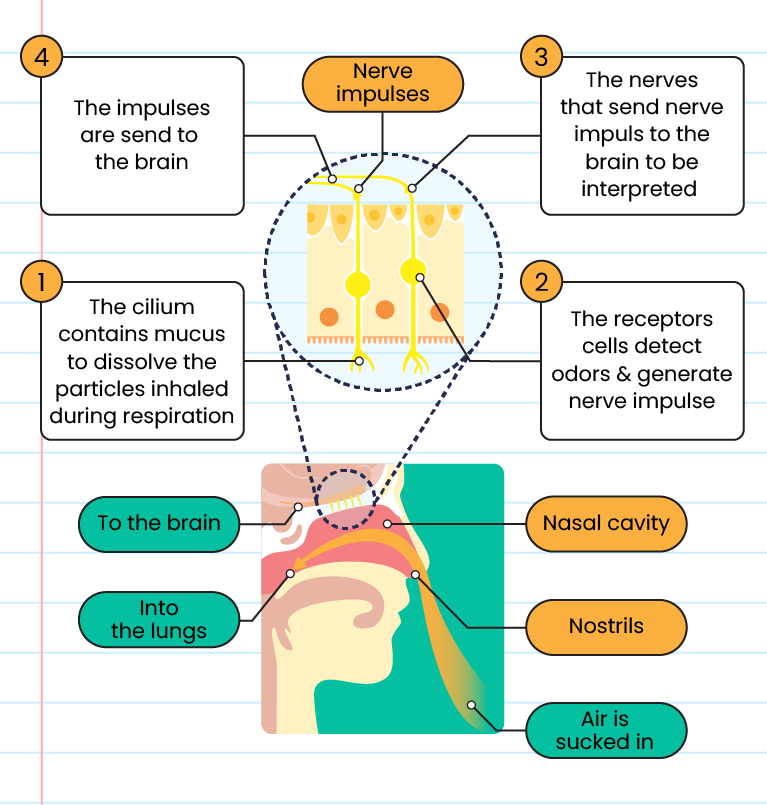
The function of the tongue:
The structure and mechanism of the tongue:
-
The surface of the tongue is covered by taste buds that contain many taste receptors and are scattered on the surface of the tongue
-
Taste receptors are sensitive to chemicals in food
-
The tongue has 5 types of taste receptors, namely sweet, sour, bitter, and umami (savory taste).
The function of the skin:
The structure of skin:

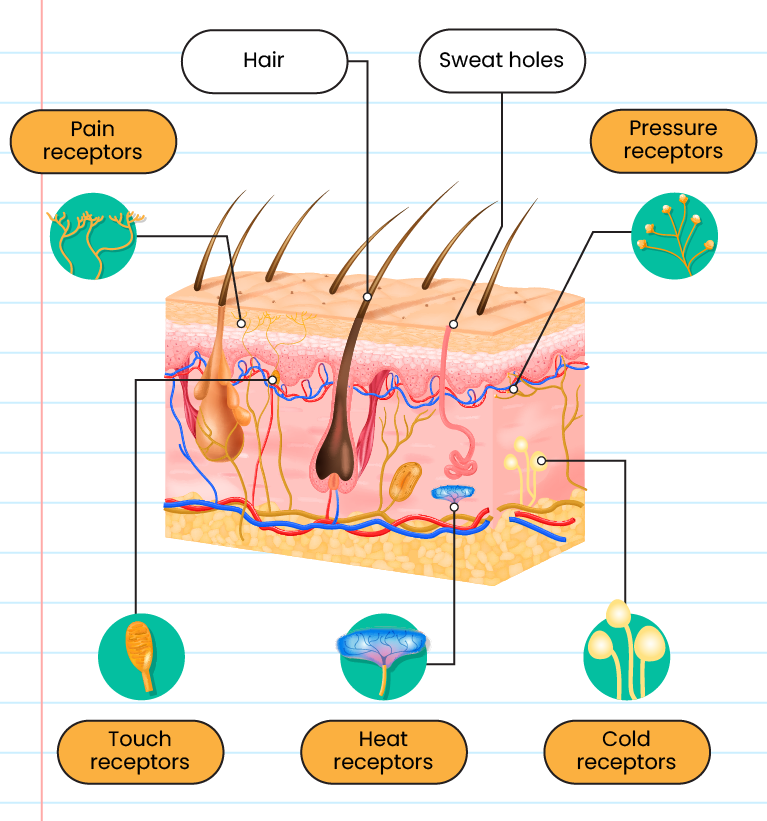
Skin sensitivity:
-
The concentration of the skin depends on the number of receptors present and the thickness of the epidermis
-
The more receptors, the more sensitive that part of the skin is
-
The thinner the epidermis, the more sensitive the skin is to stimuli
-
Blind people read Braille using their fingertips
|
Very sensitive parts of the skin
|
Part of the skin that is less sensitive
|
|
Fingertips, back of neck, lips, and earlobes
|
Elbows and knees
|
- The sensory organs are interconnected with each other and can balance the human body on a single daily basis
The limit of sensory:
The visual sensory limitations:
-
The eye cannot detect an image that falls on a blind spot
-
Human vision can also be affected due to farsightedness, nearsightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia
The structure of the normal eye, farsightedness, and nearsightedness:

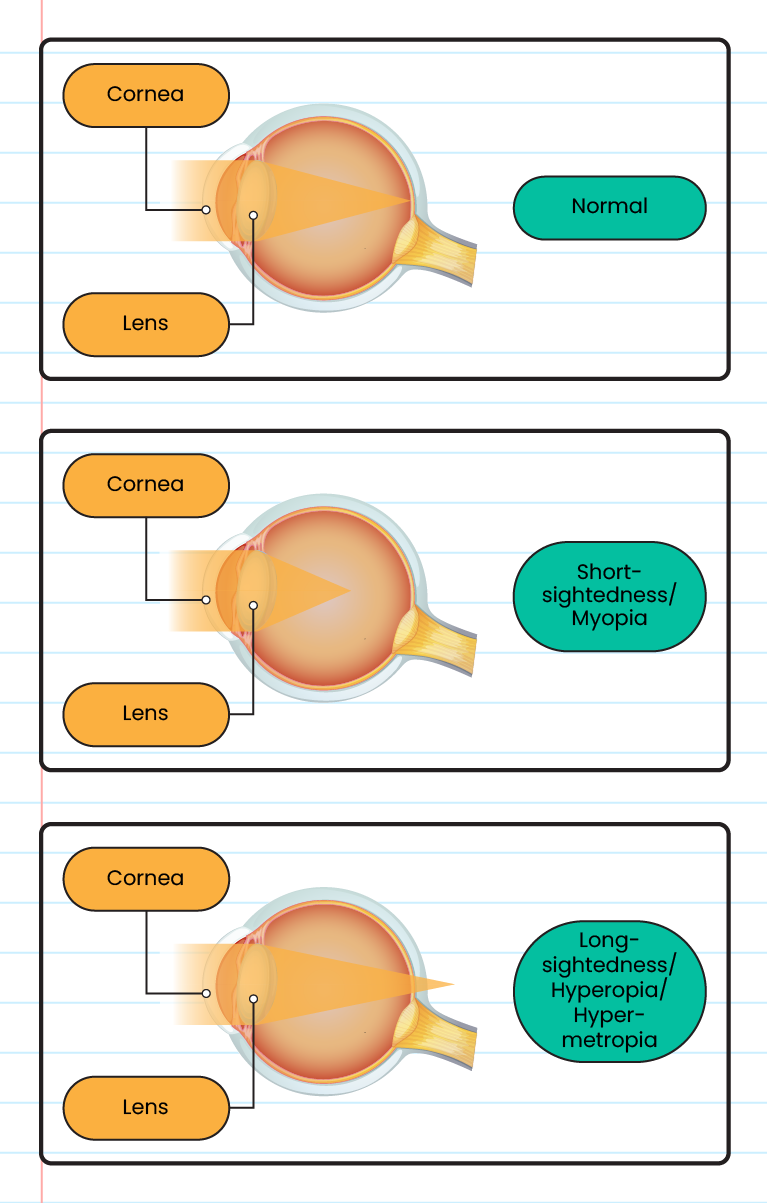
-
Farsightedness cannot see distant objects clearly because light from the object is focused in front of the retina
-
Requires a concave lens
-
Nearsightedness cannot see near objects clearly because light from the object focuses behind the retina
-
Requires a convex lens
The structure of the astigmatism eye:

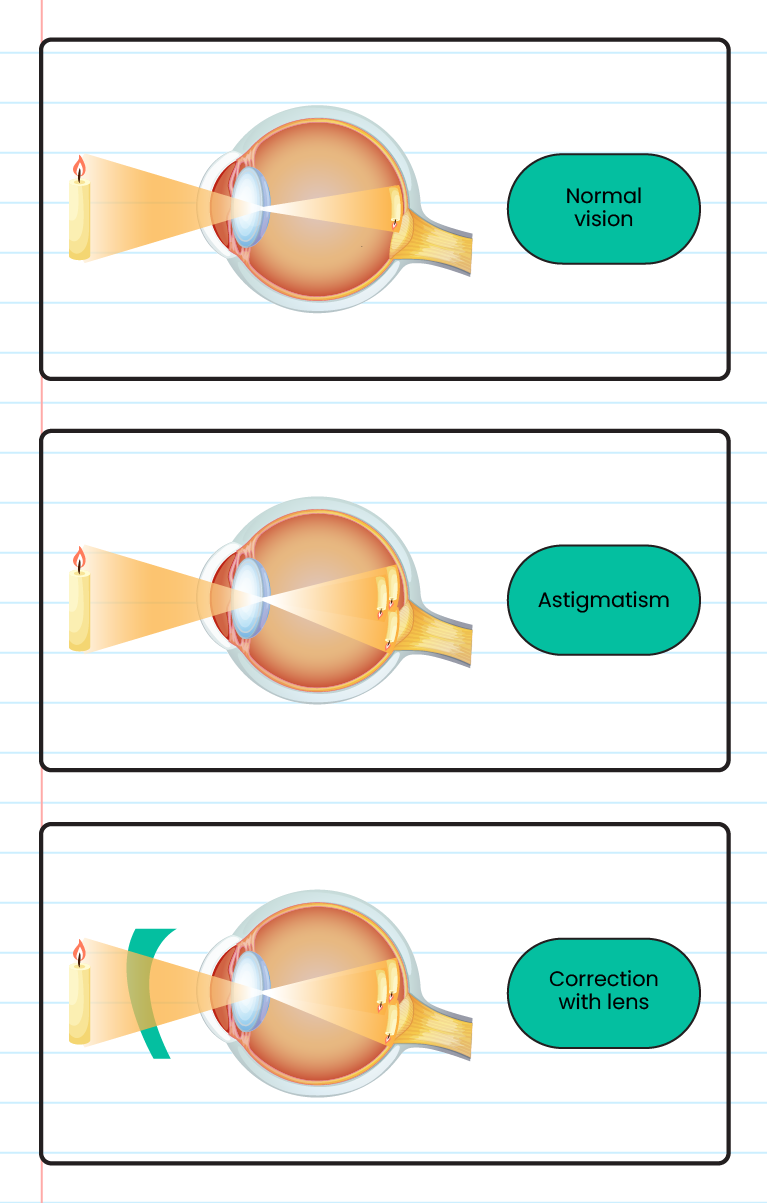
The structure of the presbyopia eye:

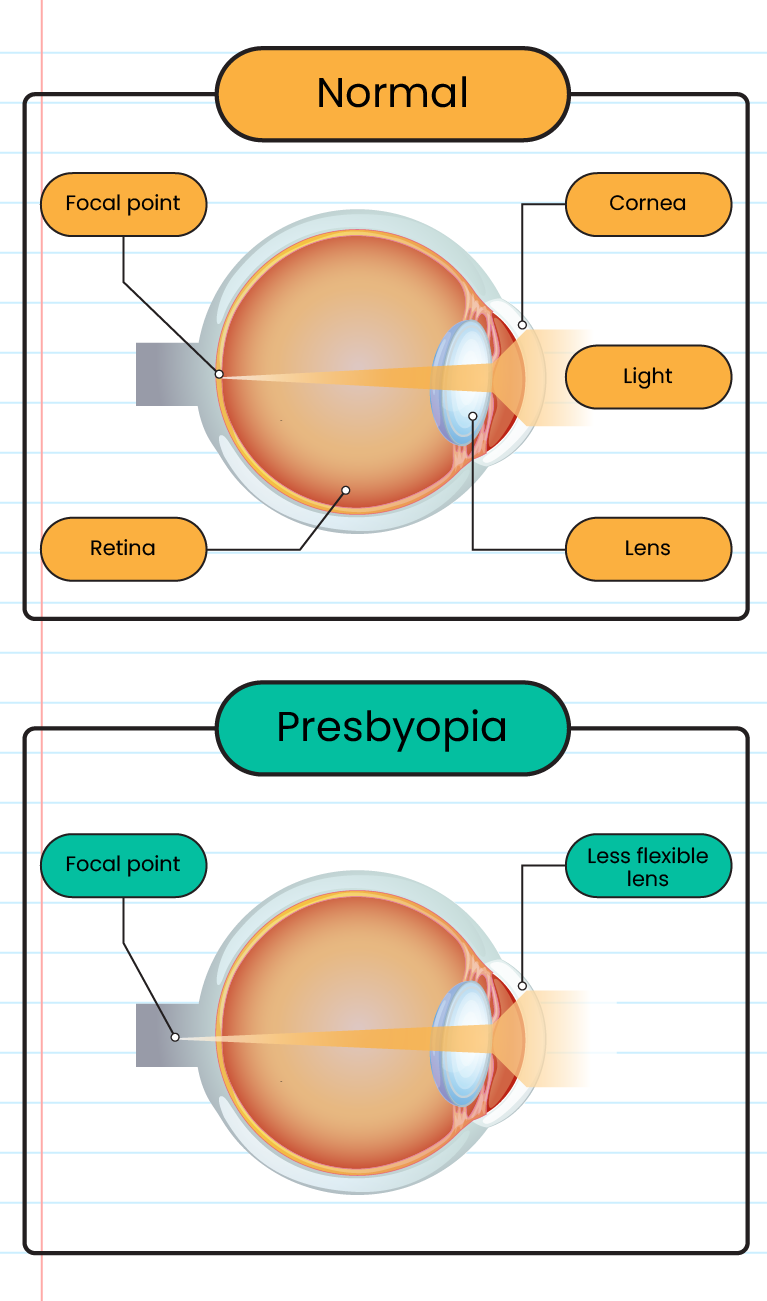
Hearing sensory limitations:
-
Humans can only hear between 20Hz to 20,000Hz
-
Deafness is caused by the ossicle bones joining together due to infection, the aging process or exposure to loud noise for a long period of time
-
Only surgery or hearing aids can help deaf people
Technology to enhance the ability of sensory organs:
| |
Technology
|
Sensory organ capacity
|
|
Limitation of vision
|
Magnifying glass & microscope
|
Can see art/small objects
|
|
Binoculars & telescopes
|
Can see distant objects
|
|
Limitation of hearing
|
Stethoscope
|
Amplifies the sound of the heartbeat
|
|
Loudspeaker
|
Amplifies the sound
|