| 2.1 |
Human Respiratory System |
| Definition |
|
The respiratory system is a respiratory system that involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide gases in the lungs
|
The structure of the human respiratory system:

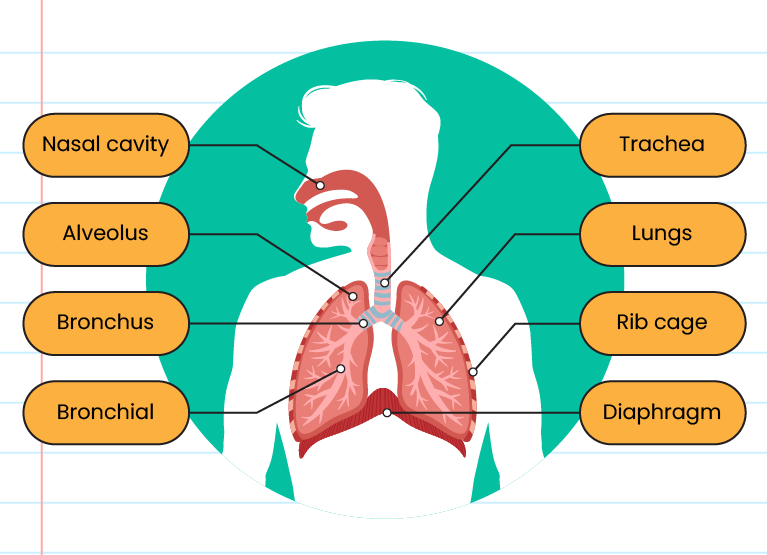
The function of each structure in the human respiratory system:
| Parts |
Structure
|
Function
|
|
Nasal cavity
|
The cavity consists of moist tissue and fine hairs
|
Moisturizes the air that passes through it as well as traps dust in the air
|
|
Trachea
|
The outer wall is made up of cartilage rings, while the inner wall is made up of epithelial cells with cilia and cells that secrete mucus
|
The cartilage ring prevents the trachea from perishing. Cilia and mucus help to trap dust and micro-organisms present in the air
|
|
Bronchus
|
Two branches of the trachea leading to the lungs
|
The air continues to the left and right lungs
|
|
Lungs
|
Soft, like a sponge, as well as rich in blood vessels and alveoli
|
Where the gas exchange takes place
|
|
Rib
|
Cage-shaped bones in the thoracic cavity
|
Protects the lungs
|
|
Diaphragm
|
Dome-shaped muscles when at rest
|
Separate the piston cavity from the abdominal cavity
|
|
Intercostal muscles
|
Muscle tissue between two ribs. It is also known as skeletal muscle
|
Move the ribs
|
The mechanisms of the human respiratory system:

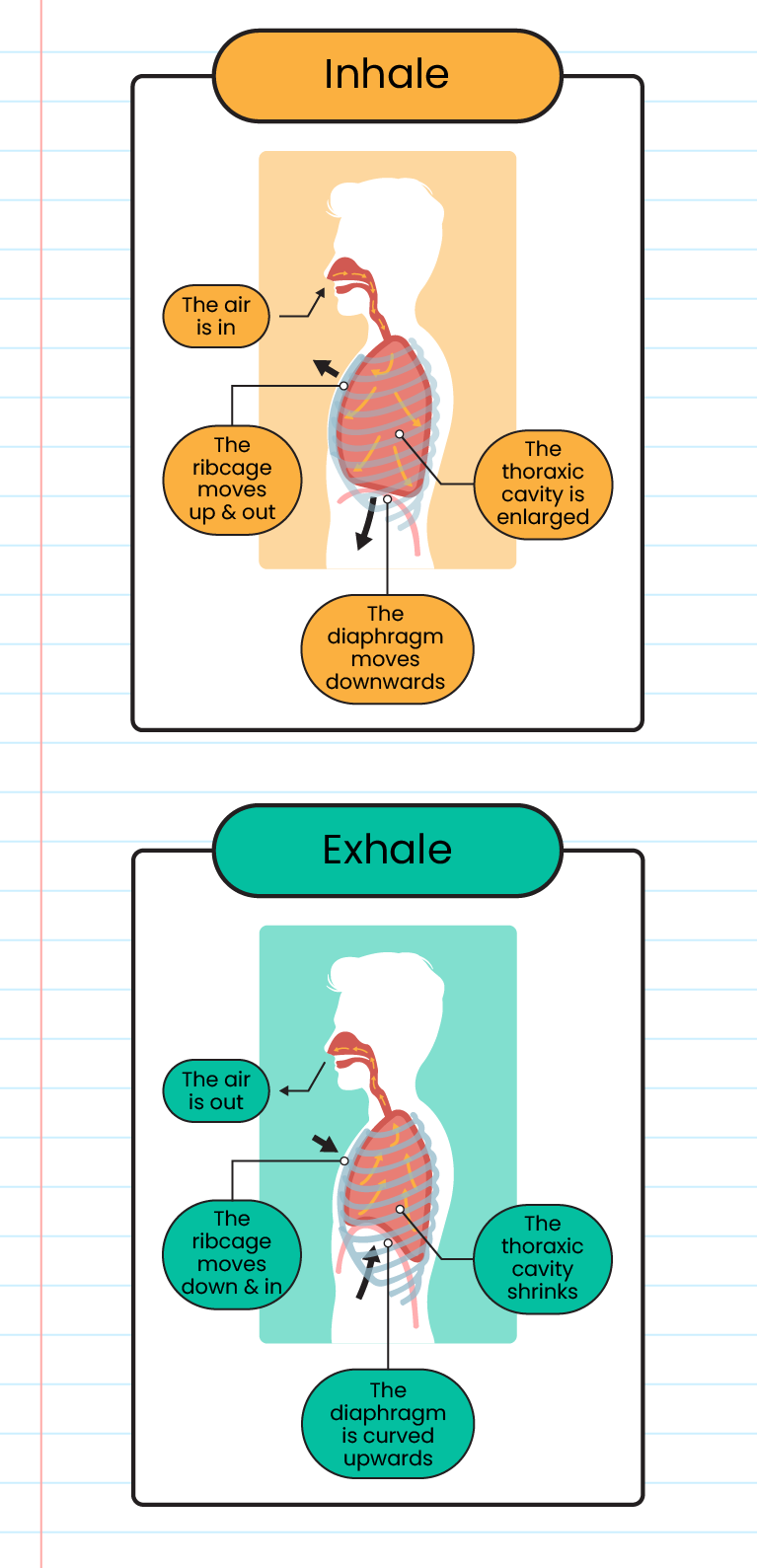
The difference between inhalation and exhalation:
|
Inhalation
|
Exhalation
|
|
The outer intercostal muscles contract
|
The outer intercostal muscles relax
|
|
The ribs move up and out
|
Rib
moving down and in
|
|
The diaphragm shrinks and flattens
|
The diaphragm relaxes and curves upwards
|
|
The volume of the thoracic cavity increases and the air pressure in the thoracic cavity decreases
|
The volume of the thoracic cavity decreases and the air pressure in the thoracic cavity increases
|
|
Air enters the lungs
|
Air is exhaled from the lungs
|
|
Oxygen content 21.0% and carbon dioxide 0.03%
|
Oxygen content 16.4% and carbon dioxide
|
The differences in oxygen and carbon dioxide content in certain parts:
|
Parts
|
Content
|
|
Oxygen
|
Carbon dioxide
|
|
Alveolus
|
High
|
Low
|
|
Pulmonary blood capillaries
|
Low
|
High
|
|
Capillary tissue
|
High
|
Low
|
|
Body cells
|
Low
|
High
|