| |
| 5.4 |
Medicine and Cosmetics |
|
| |
| Medicines |
- Definition of medicine:
- Chemicals used to help with the treatment or prevention of diseases.
- Medicines can be classified into traditional medicines and modern medicines.
- Medicines are safe if taken properly.
- Generally, medicines are for health use, but misuse or abuse of them can be harmful.
|
|
| |
| Traditional Medicines |
- Obtained from herbal plants or animals and are not chemically processed.
- Usually prepared by crushing certain parts of the plants using pestle and mortar and rubbing on sore limbs.
- There are also certain parts of the plants or animals that are boiled to get the essence and to be consumed orally.
- Nowadays, traditional medicines have evolved through processing, and marketed in the form of pills or capsules.
|
|
| |
| Examples of Plants usually used as Traditional Medicines in Malaysia |
| Source of Traditional Medicine |
Function |
| Ginseng root |
Improves health. |
| Tamarind |
The juice from its fruit can relieve cough. |
| Garlic |
Lessen infection and high blood pressure. |
| Cloves |
Relieves toothache. |
| Sirih leaves |
Relieves eyesore. |
| Turmeric |
Decreases pimples. |
| Papaya tree |
The juice can relieve skin irritation. |
| Hibiscus tree |
The leaves can relieve headache and decreases hair loss. |
| Coconut tree |
The coconut water can reduce fever. |
| Aloe vera |
The juice can reduce the pain from burned skin. |
|
| |
| Modern Medicine |
| Medicines manufactured industrially and distributed to consumers in this age. |
|
| |
|
Types of Modern Medicine
|
Function
|
Example |
|
Analgesics
|
Relives pain in conscious state.
|
- Aspirin and paracetamol
- Codeine
|
|
Antibiotics
|
Relives pain, alleviates coughs and treats diarrhoea.
|
|
| Psychotic drugs |
Stimulant
|
Stimulate and activate brain, body and emotional activity. |
- Amfetamine
- Fenilpropanolamine
|
| Antidepressant |
Treating depression.
|
|
| Antipsychotic |
Tranquiliser.
|
- Tranquiliser
- Barbiturat
- Clozapine
- Haloperidol
|
|
| |
| The Side Effect of Medicine |
|
Jenis ubat
|
Contoh
|
Kesan sampingan
|
|
Antibiotic
|
Penicilin
|
- Some might be allergic to penicillin.
- Symptoms: itchiness, shortness of breath.
|
|
Analgesic
|
Aspirin
|
- Skin rash.
- Uncosciousness.
|
| Antipsychotic |
Stimulant
|
- Addiction.
- Abuse of amphetamine.
|
|
Antipsychotic
|
|
|
| |
| Cosmetics |
- Cosmetics are substances or products used externally for cleaning, protect or beautify one's appearance.
- Various types of materials are used as ingredients in the production of cosmetics so that the desired effect is obtained.
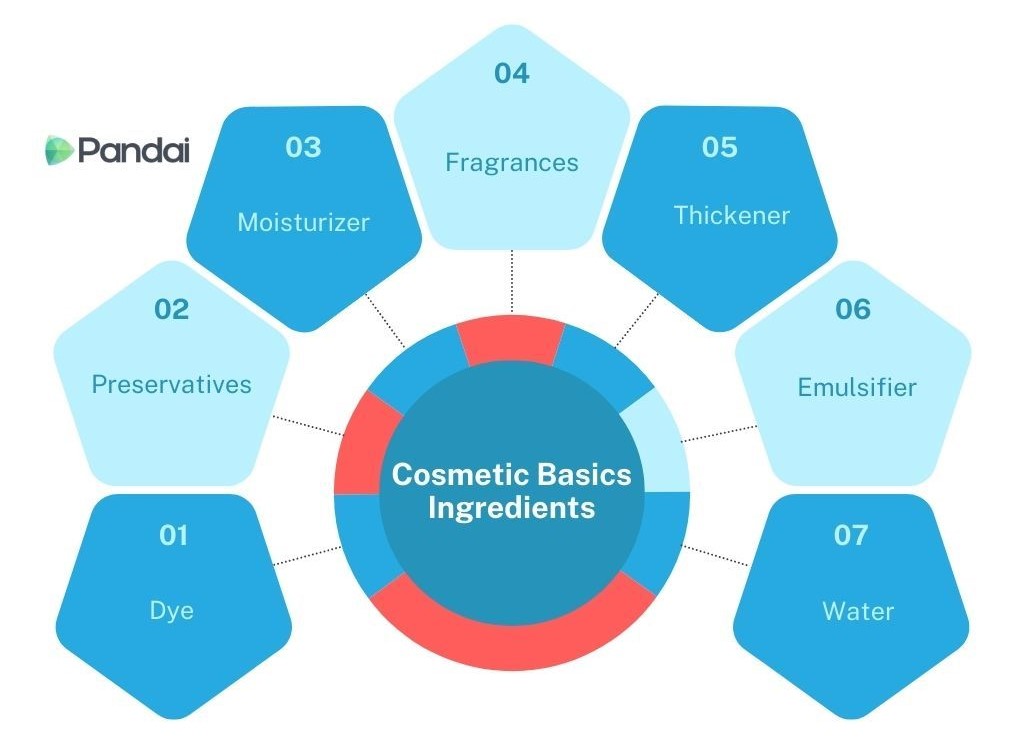
- The basic ingredients for cosmetics usually consist of a combination of ingredients such as water, emulsifiers, thickeners, dyes, moisturizers and preservatives.
|
|
| |
 |
| |
| Cosmetics Basics Ingredients |
| Dye |
- Gives colour to make cosmetics more attractive.
- Example: Iron (III) oxide.
|
| Preservatives |
- Prevent cosmetic damage.
- Examples: Parabens and formaldehyde.
|
| Moisturizer |
- Maintains the moisture of cosmetic ingredients.
- Examples: Glycerin and sodium lactate.
|
| Fragrances |
- Gives a pleasant aroma to cosmetic products.
- Example: Essential oils.
|
| Thickener |
- Thickens cosmetic products. Examples: Glycerin and xanthan gum.
|
| Emulsifier |
- Forms a homogeneous mixture between water and oil.
- Examples: Lecithin and stearic acid.
|
| Water |
- Solvents in the production of cosmetics.
|
|
| |
| Types of Cosmetics |
| Makeup cosmetics |
Used to beautify the face: Powder, lipstick, pencil eyebrows, blush, eye shadow, eyeliner and mascara. |
| Cosmetic care |
Treatment on the body: Creams, skin moisturizers and face mask. |
| Fragrances |
Fragrances: Deodorants and perfumes. |
|
| |
| The Use of Cosmetics in Life |
| Pros of Homemade Cosmetics |
Cons of Commercial Cosmetics |
|
Easily produced using natural ingredients
|
Harmful side effects
|
|
Safe and no harmful chemicals
|
There are hazardous chemicals included illegally.
|
|
Cheap cost
|
Excessively highlighted and misleading advertisement.
|
|
| |
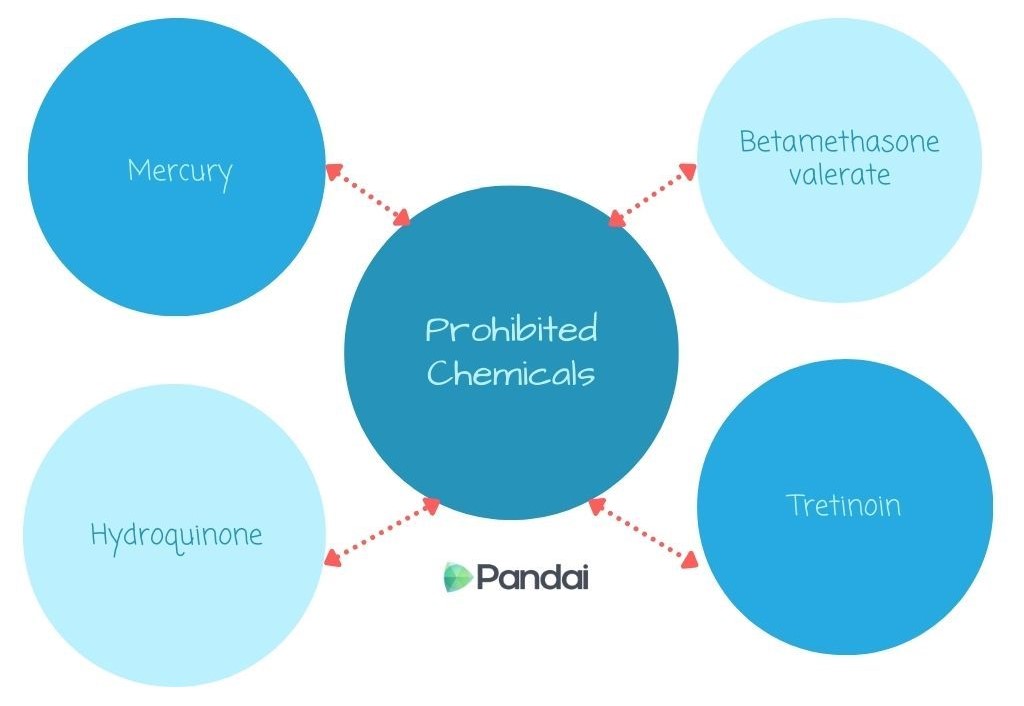
| Side Effects of the Use of Banned Chmicals in Cosmetics |
| Prohibited Chemicals |
Side Effects |
| Mercury |
Skin irritation as well as fruit damage waist and nervous system if absorbed into the bloodstream. |
| Hidroquinone |
Skin becomes hypersensitive and pigmentation reduction resulting in skin exposure to harmful UV rays. |
| Betamethasone valerate |
Skin irritation and changes in skin pigmentation. |
| Tretinoin |
Skin redness and flaking.. |
|
| |
 |
| |
| Prohibited Chemicals |
Note |
|
Mercury
|
It is usually included in whitening creams as well as other cosmetic products illegally. |
| Hydroquinone |
| Betamethasone valerate |
| Tretinoin |
Acne cream. |
|
| |