Structure and Functiion of parts of Flowers
Pollination
| Types of flower |
| Unisexual |
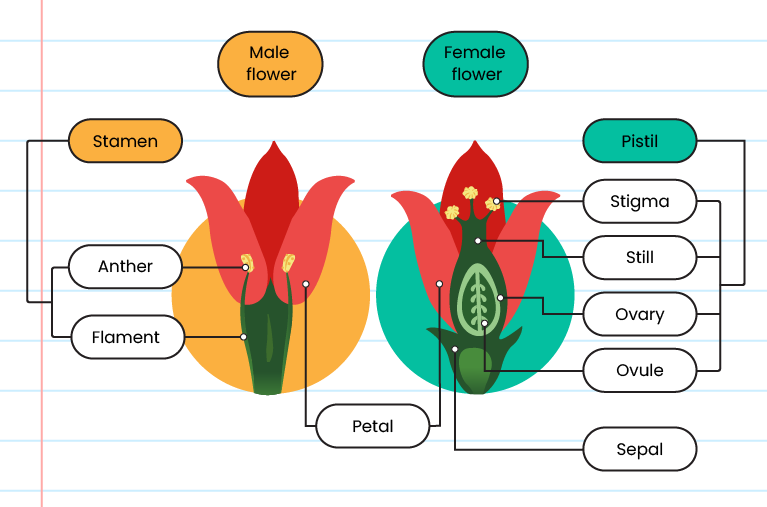 |
|
Example:
Corn flower, papaya flower
|
| Bisexual |
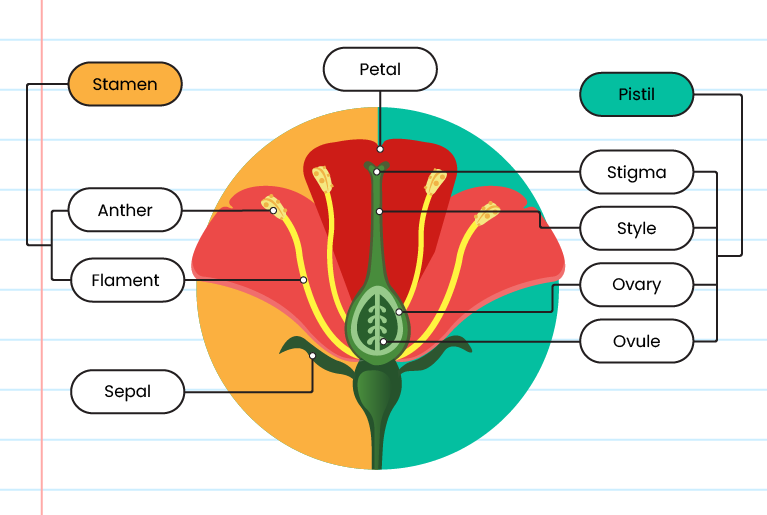 |
|
Example:
Rose and Sunflower
|
| Types of pollination |
| Self-pollination |
Cross-pollination |
- Pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of another flower on the same plant
- Pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of the same flower
|
- Pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of another flower on a differentt plant of the same species.
|
Pollinating Agents
|
Animals and insects
- Polllen grains usually stick on the beak or body of the animal.
When an insect lands on a flower to suck its nectar, pollen grains will stick to its furry feet and body.
- The characteristics of animal-pollinated and insect-pollinated flowers:
- - have big and colourful petals
- - have nectar and smell nice
- - produce rough and sticky pollen grains
- Examples of animal-pollinated flowers and insect-pollinated flowers are durian, rambutan, papaya, hibiscus, sunflower and rose.
|
|
Wind
- Light pollen grains are blown by the wind and reaches the stigma of another flower.
- The characteristics of wind-pollinated flowers:
- - have white or pale petals
- - have a long and furry stigma
- - have plenty of small, smooth and light pollen grains
- - have a long filament and style
- Examples of wind-pollinated flowers are corn, grass and paddy.
|
The Advantages of Cros-Pollination
- New plants that are more resistant to pests and diseases
- Healthier plants which can adapt better to changes in the environment
- New varieties of plants
- Good quality seeds
The Innovation of Cross-Pollination in Agriculture
| Plant and parent plants |
Hybrid plant |
Characteristics of hybrid plant
|
|
Palm oil
Pisifera and Dura
|
Tenera |
More fruits
Flesh
Thinner shell
|
|
Papaya
Subang 6 and Sunrise Solo
|
Eksotika |
Sweeter
Bigger fruits
|
Fertilisation Process
Structures of a Seed and Their Functions
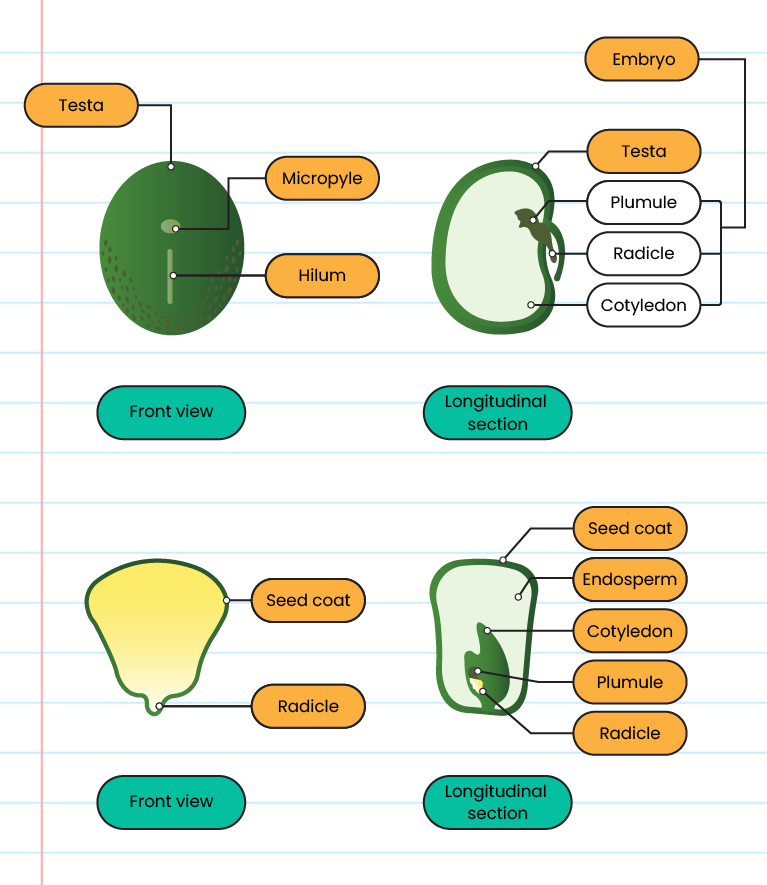
| Structure of dicotyledon |
Structure of monocotyledon |
| The structure and functions of a seed |
| Part |
Structure |
Function |
| External |
Testa |
Protects the seed |
| Hilum |
Place where the seed sticks to the frui |
| Micropyle |
Small hole to allow air and water to enter the seed |
| Embryo |
Plumble |
Part of the embryo which develops into a new
shoot |
| Radicle |
Part of the embryo which develops into the root |
| Cotyledon / Endosperm |
Stores and provides food for the seed |
Germination of Seeds
| Epigeal germination |
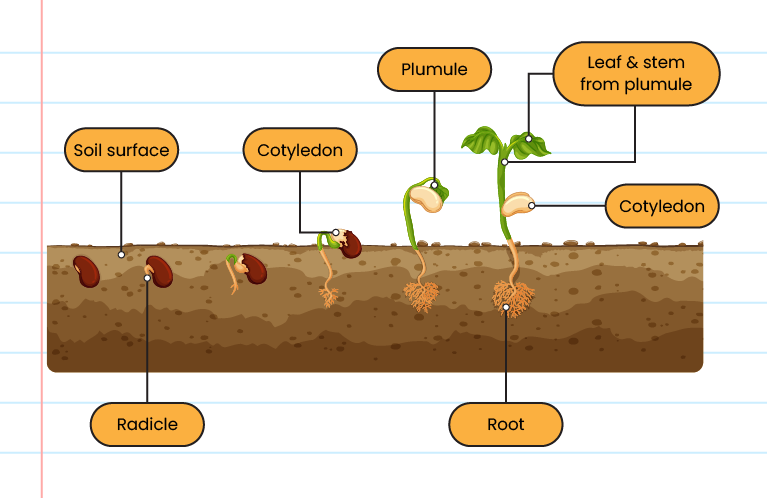 |
| Hypogeal germination |
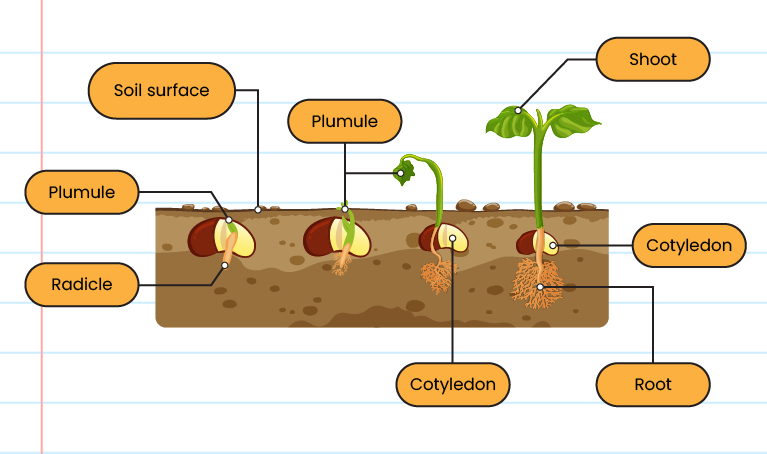 |
The Conditions Required for Germination of Seeds
- Water
- Air
- Suitable temperature