| 4.2 |
Human Reproductive System |
| Male Reproductive System |
| |
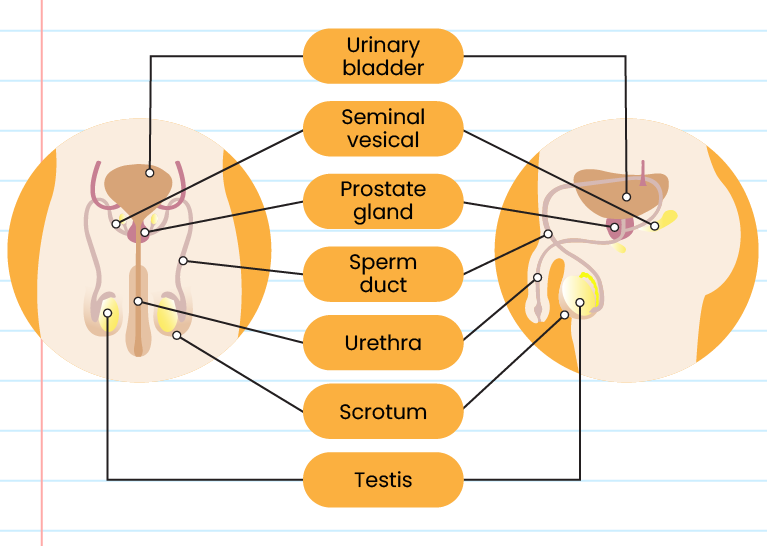 |
| Part |
Function |
| Seminal vesicle |
Secretes nutritional fluid for the sperms |
| Urethra |
A channel to discharge sperms and urine from the body |
| Sperm duct |
Transports sperms from the testis to the urethra inside the body |
| Penis |
Transfers sperms into the vagina of the female during copulation |
| Scrotum |
Holds and protects the testes |
| Testis |
Produces male gametes (sperms) and male sex hormones |
| Prostate glands |
Secrete fluid which contains nutrients and protects sperm cell |
Female Reproductive System
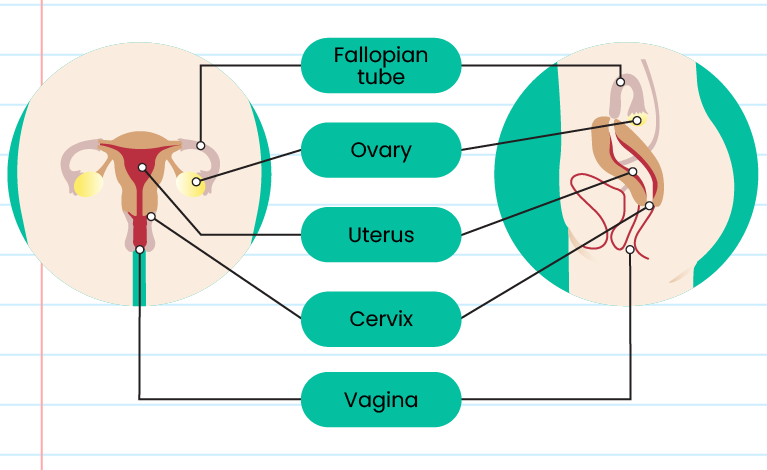
| Part |
Function |
| Fallopian tube |
Place where fertilisation between sperm and ovum occurs |
| Ovary |
Produces female gamete (ovum) and female sex hormones |
| Uterus (womb) |
Place where the embryo develops and grows |
| Cervix |
Produces mucus to enable sperms to swim into the uterus |
| Vagina |
Receives sperms and as a channel through which a baby is born |
Physical Changes that Occur During Puberty
| Male |
Female |
|
Voice
- Vocal cord (larynx) enlarges
- Voice becomes deeper
|
Body
- Breasts grow
- Hips become firm and broader
- Hair grows on the armpits
|
|
Body
- Mousthache and beard begin to grow
- Hair grows on the face, armpits and chest
|
Reproductive organs
- Ovaries produce ova and sex hormones
- Hair grows at pubic region
- Menstrual cycle begins
|
|
Reproductive organs
- Testes produce sperms and sex hormones
- Hair grows at pubic region
- Penis and scrotum enlarge
|
|
Comparison between the Male and Female Gametes
| Sperm |
Ovum |
| Able to move |
Not able to move |
| Produced by testis |
Produced by ovary |
| Male gamete |
Female gamete |
| Smallest cell in the male's body |
Largest cell in the female's body |
| Carries genetic information |
| Sexual reproductive cell |