| |
|
|
| |
|
Explaining pressure using the kinetic theory of gases.
|
- Gas molecules move freely and randomly
- Gas molecules hit wall of container and change direction (elastic collision) resulting in a change in momentum
- Change of momentum per time produce force
- Force per unit area produce pressure
|
| |
|
Factors incluencing the gas pressure
|
- Gas density
- \(\rho\;\uparrow\;P\uparrow\\ \rho\;\downarrow\;P\downarrow\)
- Temperature
- \(T\;\uparrow\;P\uparrow\\ T\;\downarrow\;P\downarrow\)
|
| |
|
Instruments to measure gas pressure
|
|
|
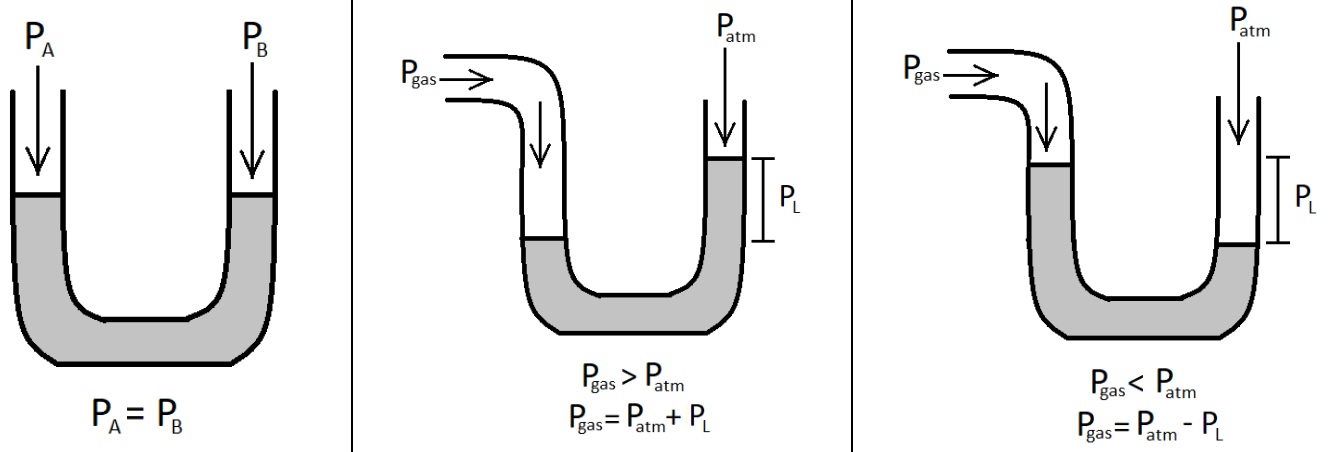 |
| |
| |
| |
Another formula for pressure |
|
| |
- \(P=\dfrac{F}{A}\), where P = pressure, F = force , A = area.
- \(P\propto\dfrac{1}{A}\rightarrow P\text{ is inversely proportional to }A\)
- \(A\uparrow\;\;P\downarrow\)
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| |