| |
|
|
| |
| |
Semiconductor |
|
| |
A group of materials that conduct electricity better than an insulator but less efficient than metal conductors.
Elements commonly used as semiconductors include silicon, germanium and selenium.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
Doping process |
|
| |
Process of adding small amounts of foreign atoms such as antimony and boron atoms.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Types of semiconductors
|
- n-type semiconductor
- Silicone (4 valence electrons) is doped with pentavalent atoms such as antimony, phosphorus or arsenic to increase the number of free electrons.
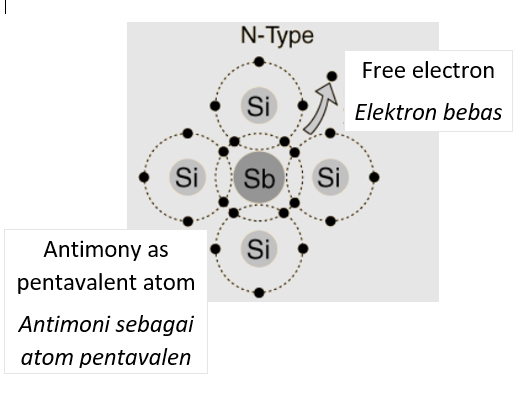 - This silicone has electrons as the majority charge carrier.
- p-type semiconductor
- Silicone is doped with trivalent atoms such as boron, indium and gallium which have more positive holes.
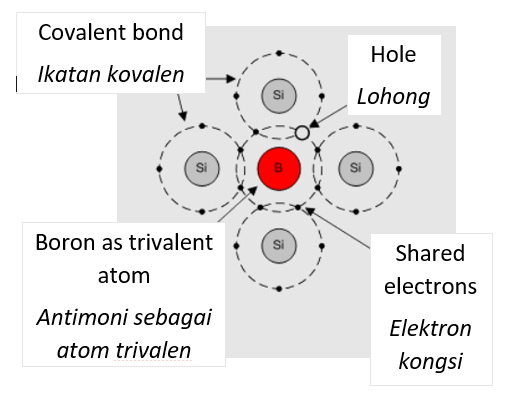 - This silicone has a positive hole as the majority charge carrier.
|
| |
| |
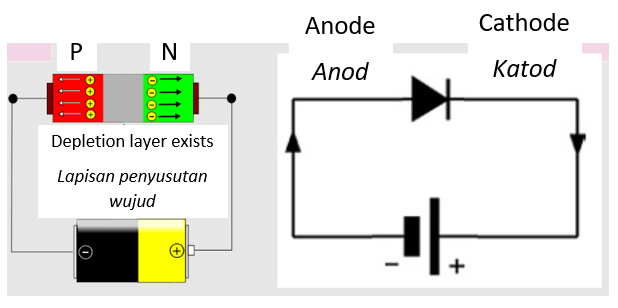
Semiconductor diode |
|
| |
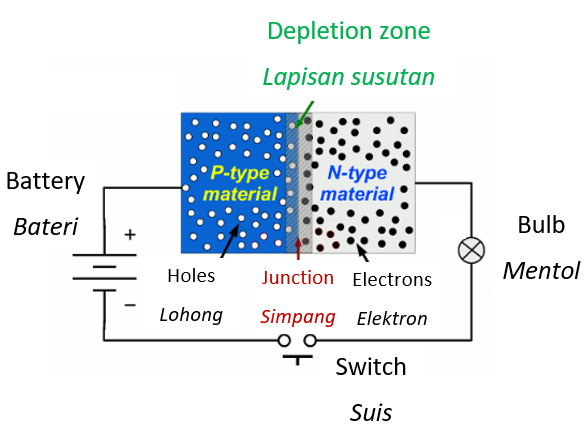
It is obtained when the p-type and n-type semiconductors are combined.
It acts as a tool that allows the current to flow in one direction only.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| |
| |
|
The diode works in two ways:
|
| |
- Forward-biased
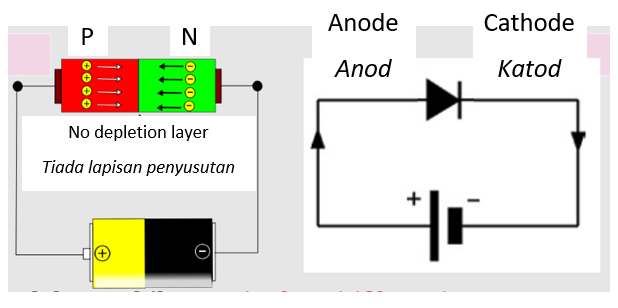 -
The depletion layer shrinks, R decreases
-
The junction voltage decreases
-
The supplied V is higher than the junction voltage
-
Current flows
-
Reverse-biased
-
-
The depletion layer thickens, R increases
-
The junction voltage increases
-
The supplied V is lower than the junction voltage
-
Current does not flow
|
| |
| |