| |
|
|
| |
| |
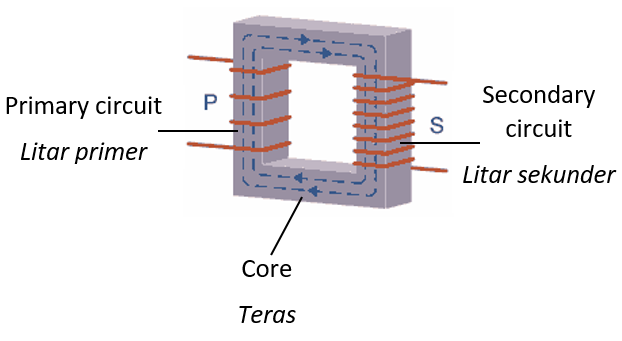
Transformer |
|
| |
A tool that can increase or decrease the capacity of the alternating current supply. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| |
|
There are two types of transformers which are step-up transformer and step-down transformer.
|
| |
- Step-up transformer
- Increase the potential difference or voltage.
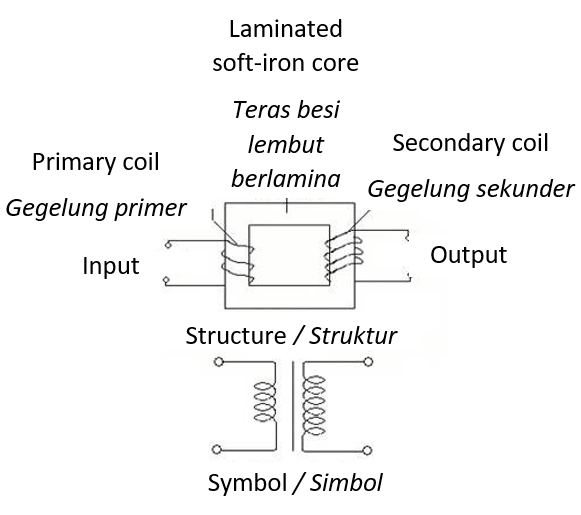 - \(V_s > V_p\), \(N_s > N_p\) , \(I_s < I_p\)
- Step-down transformer
- Lower the potential difference or voltage.
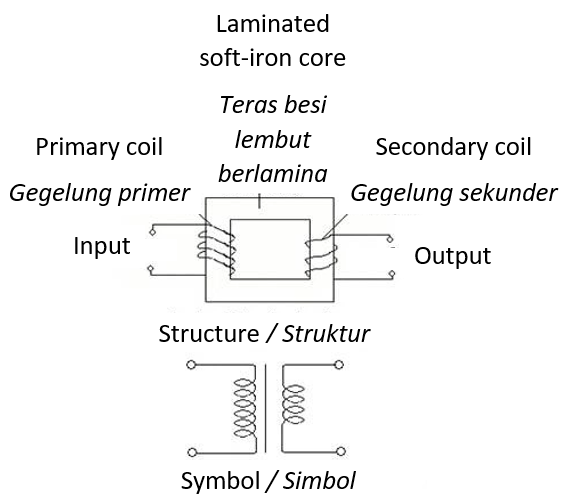 - \(V_s < V_p\), \(N_s < N_p\), \(I_s > I_p\)
|
| |
| |
Transformer formula |
|
| |
\(\dfrac {V_s}{V_p} = \dfrac {N_s}{N_p}\), where V = voltage and N = number of turns |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
Ideal transformer |
|
| |
A tool used to efficiently convert the input power to the output power without any heat loss to the environment.
It has \(100 \%\) efficiency.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
Formula |
|
| |
\(\begin {aligned} \text {Output power} &= \text {Input power} \\ P_s &= P_p \\ V_s \space I_s &= V_p \space I_p, \end {aligned} \)
\(\begin {aligned} \text {Efficiency} &= \dfrac {\text {Output power}}{\text {Input power}} \times 100\% \\ &= \dfrac {V_s \space I_s}{V_p \space I_p} \times 100\%. \end {aligned}\)
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |