| |
|
|
| |
| Introduction to Leaf |
- Leaf is the main organ of a plant which carries out photosynthesis.
- The structure of a leaf can be divided into two parts, which are:
- The external structure.
- The internal structure.
|
|
| |
| The External Structure of a Leaf |
- Lamina is the flat, thin, smooth and green part of the leaf.
- Lamina is flat-shaped to provide a wide surface in order to expose the cells containing chloroplasts to the maximum amount of sunlight.
- Lamina is also thin to allow gases involved in photosynthesis to diffuse efficiently in the leaf.
|
- Vascular tissues in vein transport water,mineral salts and photosynthesis products continuously and effectively.
- The network of vein combines to form a main vein and connects to vascular tissues of stem through petiole.
- Petiole is the leaf stalk that connects the lamina to the stem of the plant.
- The petiole stretches out into the lamina producing a network of middle veins to support the lamina.
|
|
| |
| The Internal Structure of a Leaf Lamina |
- In most plants, the leaves grow without overlapping to enable them to receive optimum light to carry out photosynthesis.
- Such arrangement is called leaf mosaic.
- The diagram below shows the internal structures of a leaf lamina.
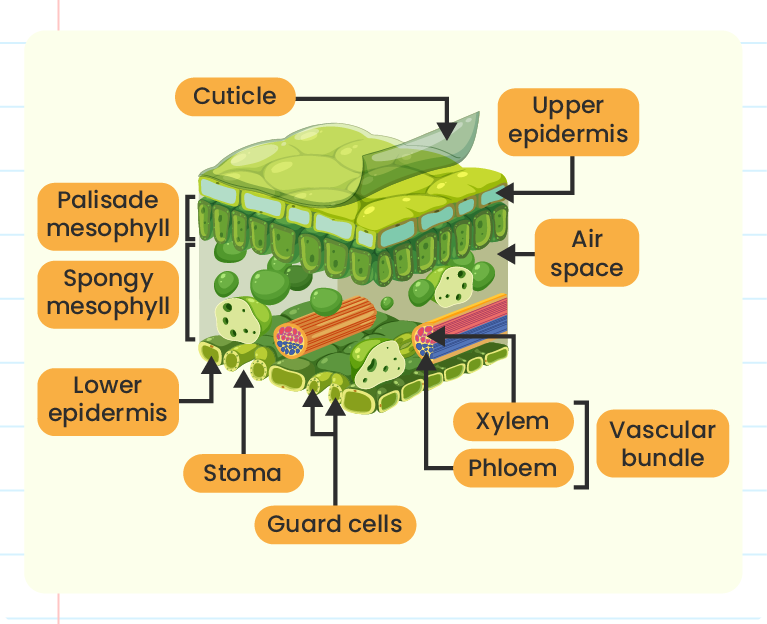
|
|
| |
 |
| |
| Structure of A Leaf |
Function |
| Epidermis |
- A transparent layer allows sunlight penetration into leaf.
- Secretes cuticle to reduce water loss from leaf.
- Protects leaf tissues from injury and entry of pathogens.
|
| Palisade mesophyll |
- Cylindrical shaped of cells which contain chloroplasts.
- Can carry out photosynthesis.
- Closely arrangement of palisade mesophyll cells to absorb sunlight maximally for photosynthesis.
|
| Spongy mesophyll |
- Irregular shaped of cells which contain chloroplasts.
- Can carry out photosynthesis.
- Loosely arrangement of spongy mesophyll cells to form air spaces for carbon dioxide and water evaporation.
|
| Xylem |
- Transport water and mineral salts from roots to leaf.
|
| Phloem |
- Transport organic products from leaves to other parts of plants.
|
| Vascular bundle |
- Component of vascular tissue in plants consisting both phloem and xylem.
|
| Guard cell |
- Kidney shaped cells on leaf epidermis.
- Two guard cells join at both cellll ends to form a stoma.
- Control opening and closing of stomata for gaseous exchange and transpiration.
|
|
| |