| |
| 5.5 |
Application of Nanotechnology in Indutry |
|
| |
| Definisi of Nanosscience |
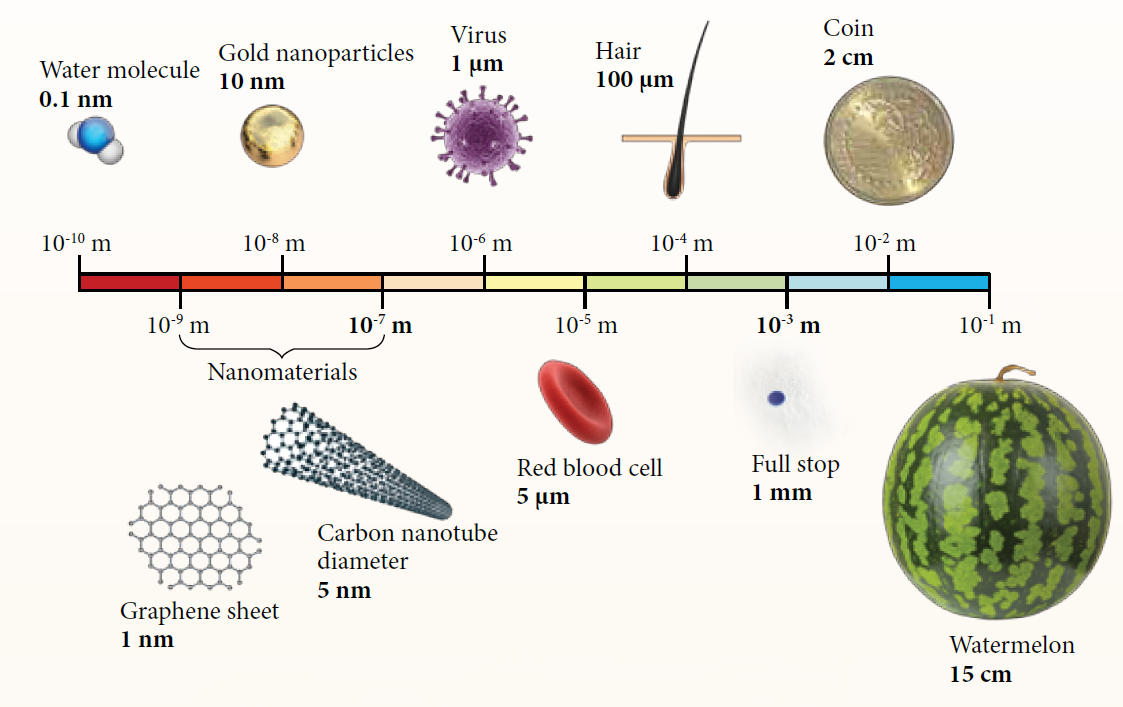
| Study on the processing of substances at the nanoscale that is between 1 nanometre and 100 nanometres. |
|
| |
| Definisi of Nanotechnology |
| Development of substances or gadgets using the properties of nanoparticles. |
|
| |
| Size Comparison between Different Materials |
 |
|
| |
 |
| |
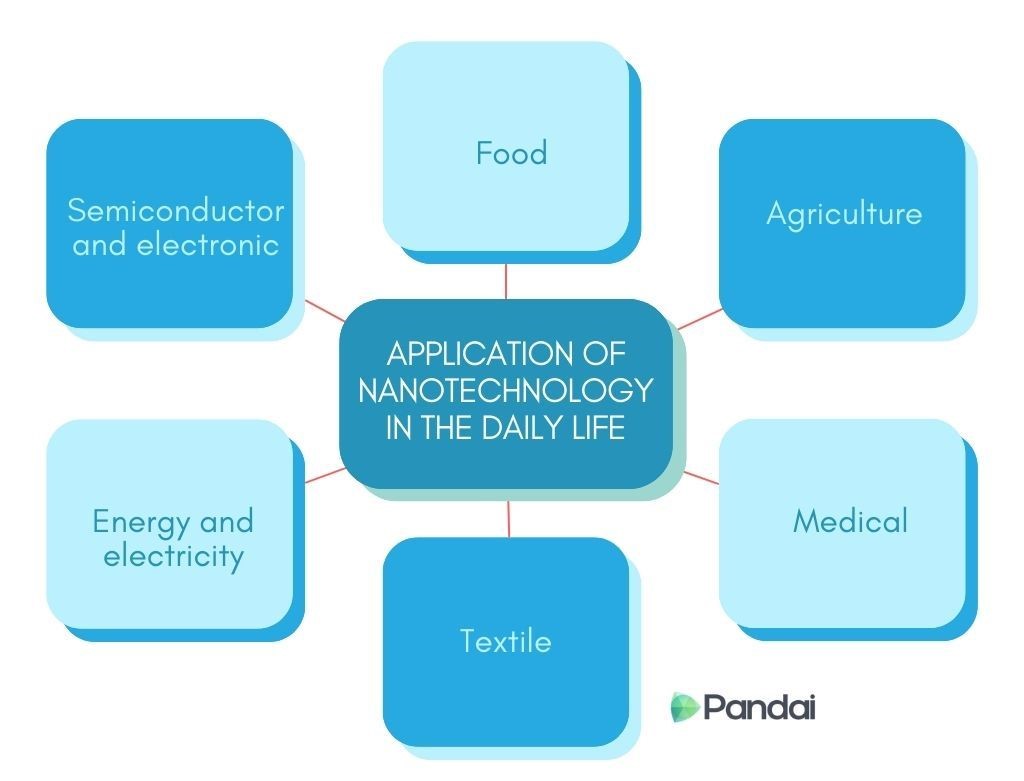
| Application of Nanotechnology in Daily Life |
| Semiconductor and Electronic |
- Smaller and more efficient semiconductors.
- High conductivity wiring system.
|
- Smaller and more efficient solar cells.
- Long-lasting batteries.
|
- Water, fire and dirt resistant fabrics.
- Ani-wrinkle and UV protective fabrics.
|
- Highly sensitive testing devices.
- More effective drug delivery system.
|
- More effective pesticides.
- Highly efficient and thorough fertilisation.
|
- Nanoscale food additives.
- Anti-microbial food packaging.
|
|
| |
| Development in the Field of Nanotechnology |
- The coverage of the field of nanotechnology is very wide, crossing various disciplines, including:
- Physics
- Chemistry
- Biology
- Medicine
- Engineering
- This contributes to the rapid research and development on applications of nanotechnology in various aspects of life.
- As an example, a material that has become one of the main focuses is:
- A carbon derivative that is known as graphene.
- Graphene is one of the carbon allotropes, other than diamond and graphite, but has different characteristics from the rest.
- The size of graphene measures from 0.1 nm, which makes graphene among the most important materials in nanoscience and nanotechnology.
- Graphene sheets can be converted into other materials, including graphites, carbon nanotubes and fullerene balls.
|
|
| |
| Graphene |
- Graphene is one of the allotropes for carbon besides diamond and graphite.
- Yet they have very different properties from each other
- The 0.1 mm size of graphene makes graphene one of the important materials in the field of nanoscience and nanotechnology.
- Graphene sheets can produce a variety of other materials including:
- Graphite
- Carbon nanotubes
- Fullerene balls
|
|
| |
 |
| |
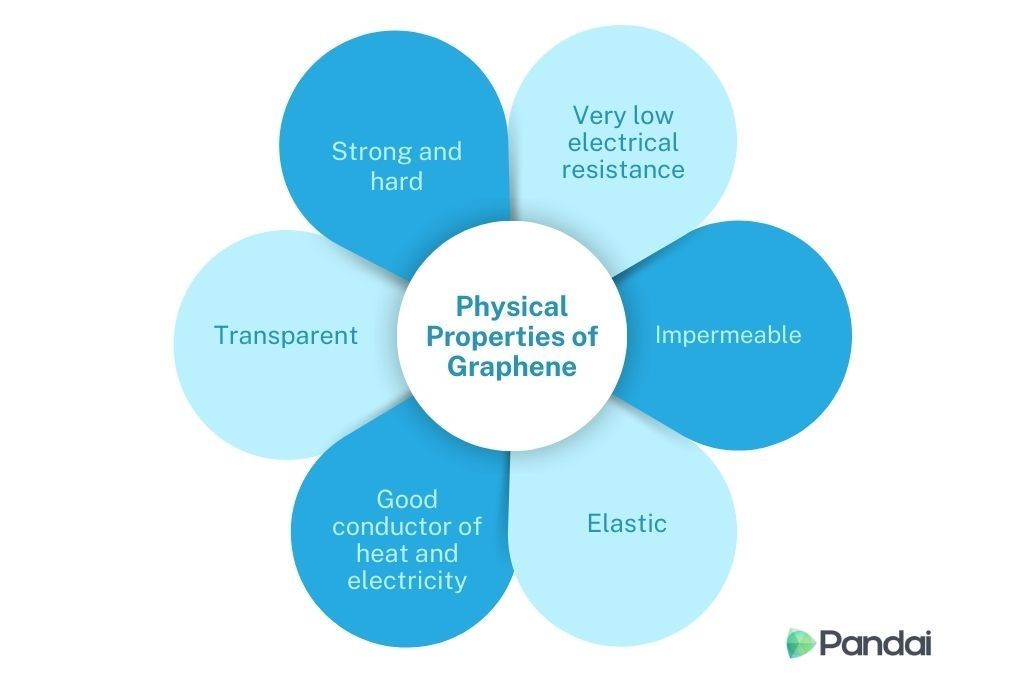
| Chemical Properties of Graphene |
- Graphene sheets burn at a lower temperature than graphite
- The most reactive carbon allotropes.
- The chemical reaction of graphene is still being studied by researchers.
|
|
| |
| Uses of Graphene |
- The arrangement of atoms in graphene makes it a superior conductor.
|
- Graphene has a high surface area.
|
- Sensors, tissue engineering, drug delivery systems.
|
- The high mechanical strength makes graphene suitable as a polymer composite material.
|
- Water filtration.
- Separation of water from gas mixtures.
|
- Longer lasting, flexible and powerful battery.
- Supercapacitor.
|
|
| |